
 C
C


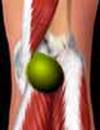
 CYST POPLÍTEO Or DE BAKER
CYST POPLÍTEO Or DE BAKER


|
 C
C
|

|

|
 CYST POPLÍTEO Or DE BAKER
CYST POPLÍTEO Or DE BAKER
|

|
| CYST POPLÍTEO Or DE BAKER |





 CYST POPLÍTEO Or DE BAKER
CYST POPLÍTEO Or DE BAKER

U.E.P.
 Add to Favorite
Add to Favorite
 Home Page
Home Page
 Recommend this Page
Recommend this Page
|

|
|
2008 © HIPERnatural.COM
www.hipernatural.com Your Source of Natural Health in Internet |
|